What Is 3D Printing? How a 3D Printer Works and Its Applications
The Amazing World of 3D Print: Exploring 3D Printers and Their Endless Possibilities
3D print technology has revolutionized the way we design, prototype, and manufacture products. From creating intricate prototypes to printing functional parts, the use 3d printing has become a game-changer across various industries. This article delves into the captivating world of 3d print, exploring what it is, how 3d printers work, and the limitless applications of this transformative technology. This comprehensive 3d printing guide is designed to help you better understand the different printer types, the various 3d printing techniques and the diverse range of benefits. Whether you’re a curious beginner or an industry professional, this article is a must-read for anyone eager to explore the fascinating capabilities of 3d print.
Article Outline:
- What Exactly is 3D Print?
- How Does a 3D Printer Work?
- What are the Different Types of 3D Printing Technologies?
- What are the Main Benefits of 3D Printing?
- What are the Various Applications of 3D Printing?
- How is 3D Printing Being Used in Different Industries?
- What are the Common Materials Used in 3D Printing?
- How does the Cost of a 3D Printer Impact Accessibility?
- What is the 3D Printing Software Used in the Design Process?
- What is the Future of the 3D Printing Industry?
Article Content:
1. What Exactly is 3D Print?
3D print, also known as additive manufacturing, is a manufacturing process that builds three-dimensional objects layer by layer from a digital 3d model. Unlike traditional manufacturing methods which involve cutting away from a solid block of material, 3d printing is an additive process. Instead of removing material, 3d printing adds material to create the desired shape. This additive manufacturing process allows for the creation of complex geometries and intricate designs that might be impossible to achieve using traditional methods. The term 3d print can refer to both the process itself and the objects created by the process.
The history of 3d printing dates back to the early 1980s, but it has only recently gained mainstream attention due to the development of more accessible and affordable 3d printers. This technology allows for the creation of custom parts and functional prototypes with relative ease and speed. 3d print enables designers and engineers to quickly turn ideas into physical objects. The printing process itself starts with a 3d model, and this 3d model is used to control the 3d printer. The 3d printer then deposits layers of material to create the object.
2. How Does a 3D Printer Work?
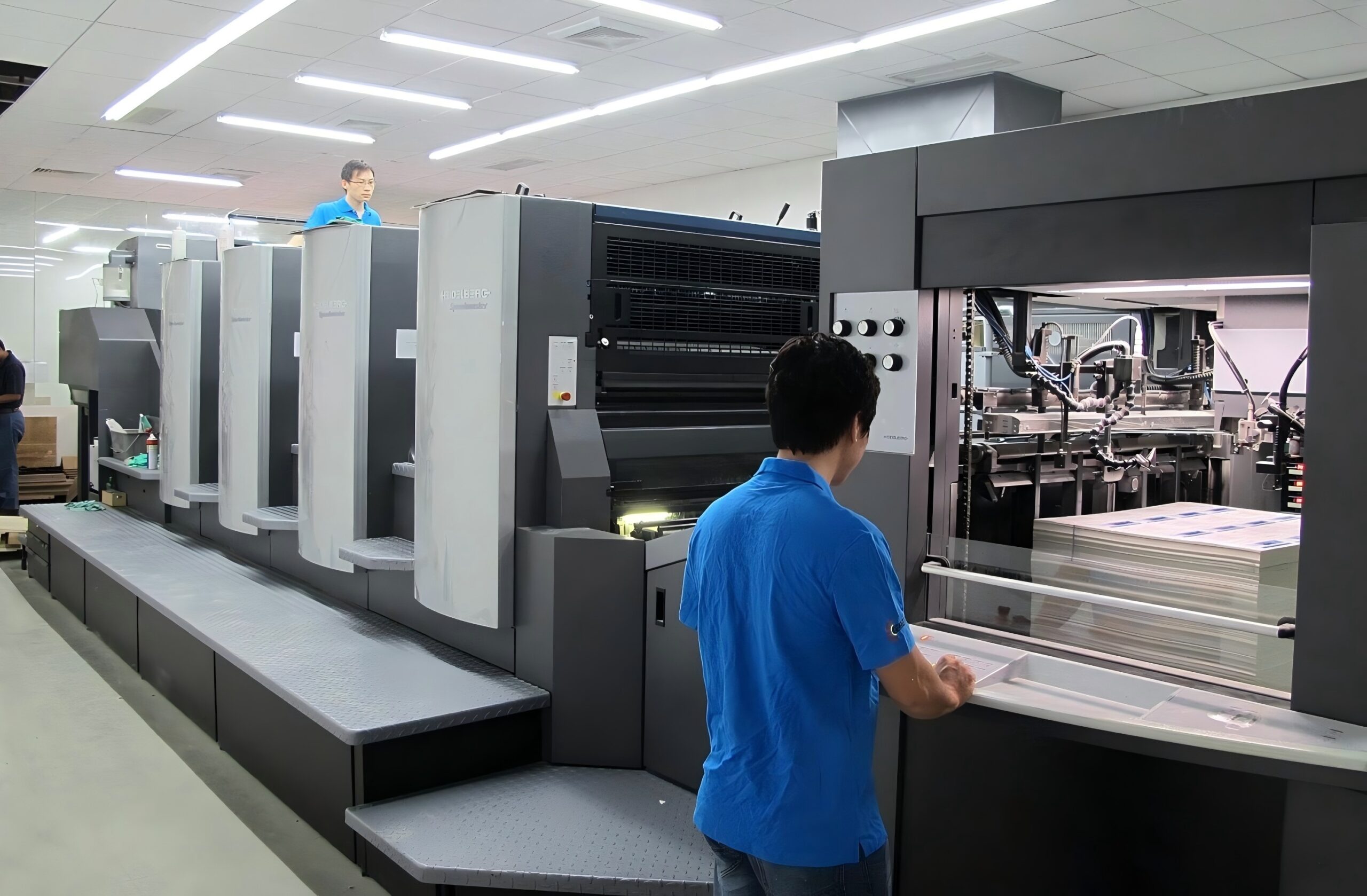
A 3d printer works by depositing layers of material, one on top of another, to create a 3d object based on a digital 3d model. This 3d model is created using specialized 3d printing software. The printer works by first heating the material and then depositing the molten material onto a build platform. The printer then moves based on the 3d model design, and deposits the material in specific locations. This printing process continues until the 3d printed part is complete.
Different 3d printers use different methods and materials to deposit the layers of material. Fused deposition modeling (fdm) 3d printers use a filament of plastic, melting it as it is fed through the printer’s nozzle. Stereolithography (sla) 3d printers use a liquid resin that hardens when exposed to light. The key idea is that the 3d printer builds up layers of material to form the three-dimensional object. The printer uses the information contained in the digital design to precisely control the deposition of each layer to achieve the final shape of the 3d printed object.
3. What are the Different Types of 3D Printing Technologies?
There are several different 3d printing technologies, each with its own unique approach to the printing process. Fused deposition modeling (fdm), also known as fused filament fabrication (fff), is one of the most common types of 3d printers. These printers melt a plastic filament and extrude it through a nozzle to create 3d printed objects. FDM 3d printers are often used for rapid prototyping because they are relatively simple and affordable. FDM 3d printing is widely used due to its accessibility and ease of use.
Another common 3d printing technique is stereolithography (sla), which uses a liquid resin that is hardened by a light source, such as a laser. This method provides higher resolution and a smoother surface finish compared to FDM. Selective laser sintering (sls) is another type of 3d printer, which uses a laser to fuse powdered materials together. This 3d printing technology is often used for printing stronger, more durable 3d printed objects. The type of 3d printer used depends on the specific requirements of the 3d printing work.
4. What are the Main Benefits of 3D Printing?
There are many benefits of 3d printing, which have made it a widely adopted manufacturing method. One of the key benefits of 3d printing is its ability to create complex geometries and designs that would be difficult, or impossible, to create using traditional manufacturing methods. Furthermore, 3d printing enables the rapid production of prototypes. This can reduce lead time by allowing designers to quickly test and iterate on their designs. By quickly creating prototypes, this can significantly reduce the development time for a new product.
Furthermore, 3d printing enables the production of customized products. This allows for the manufacture of parts tailored to the specific needs of each individual. This can make it easier to print spare parts on demand, reducing the need for large inventories. It also greatly speeds the 3d printing to develop new products. Also, 3d printing is an additive manufacturing process, therefore it produces less material waste compared to traditional manufacturing methods, such as subtractive manufacturing methods. Therefore, 3d printing is not only faster and more adaptable, but also more environmentally friendly.
5. What are the Various Applications of 3D Printing?
The applications of 3d printing span a wide variety of fields, demonstrating the versatility and adaptability of the technology. The use 3d printing to create prototypes is one of the most important applications. The ability to quickly create and test product designs makes 3d printing an essential tool for product development. Another key application of 3d printing is in the production of customized tools and parts for industrial use. The ability to make these parts quickly and easily can speed up production times.
3d printing is also used in the medical field, where it is used to create customized implants and prosthetics, as well as anatomical models for surgical planning. It can also be used to print spare parts on demand. Other unique applications include the 3d printing of houses and even organs and body parts using specialized materials. The use of 3d printing is rapidly expanding, and the technology’s adaptability means there will be an increasing number of new applications in the years to come.
6. How is 3D Printing Being Used in Different Industries?
3d printing is being used in a number of different industries, transforming manufacturing methods and creating new opportunities. The aerospace industry uses 3d printing to create lightweight, complex parts for aircraft and spacecraft. The ability to make these parts quickly and easily with an additive manufacturing process is a major benefit. The automotive industry uses 3d printing to develop prototypes and create custom parts for vehicles. This is also great for design and engineering, and can speed up the development of new vehicles.
The medical field uses 3d printing to create custom prosthetics, implants, and surgical tools. In the consumer goods sector, 3d printing is being used to develop customized products. The 3d printing industry is growing rapidly as more companies are printing functional parts, tools, and other goods. The use 3d printing can improve production efficiency, reduce material waste, and develop better designs. The integration of 3d printing is transforming manufacturing as more companies leverage the capabilities of 3d printing.
7. What are the Common Materials Used in 3D Printing?
The materials used in 3d printing vary depending on the printing technology and the specific application. Many common 3d printers use plastic filaments, such as PLA (polylactic acid) and ABS (acrylonitrile butadiene styrene). These materials are relatively inexpensive, easy to use, and suitable for a wide range of 3d printed objects. PLA is a biodegradable plastic made from renewable resources, making it a more environmentally friendly option. ABS is a stronger plastic that is ideal for parts with increased resistance.
Resin 3d printing, such as sla, uses liquid resins that are cured with light. These resins offer high levels of detail and are used for more intricate 3d printed models. Some 3d printers can also print with more specialized materials like ceramics, metals, and even concrete for 3d printed houses. The choice of 3d printing materials depends on the requirements of the 3d printed part and the printer’s capabilities. The materials continue to evolve, allowing more capabilities and better quality for the 3d printed objects.
8. How does the Cost of a 3D Printer Impact Accessibility?
The 3d printer cost has a significant impact on its accessibility for a wide range of users. In the past, the cost of 3d printers was very high, limiting their use to larger corporations or research institutions. The availability of more affordable 3d printers means that more and more individuals and smaller businesses can now access the technology. Desktop 3d printers are now available at a range of price points, making 3d printing more accessible than ever before.
The cost of the printer is not the only factor that impacts accessibility, the cost of materials, 3d printing software, and other accessories can add to the overall expense. However, as the technology continues to develop, these costs will likely continue to decrease, making 3d printing even more accessible. The reduction of the printer cost and other accessories has allowed more individuals to explore this technology and discover the various capabilities of 3d printing. The printing process will continue to be streamlined, and this will help continue to reduce the price of ownership for 3d printers.
9. What is the 3D Printing Software Used in the Design Process?
3d printing software is an essential tool for creating the 3d models required for 3d printing. This 3d printing software can range from simple design tools to highly advanced cad and 3d modeling applications. The 3d printing software also includes slicer programs that convert the 3d model into instructions for the 3d printer. This is the software that prepares the 3d design for the printing process. These slicer programs will tell the printer exactly where to deposit each layer of material.
The 3d printing software includes a variety of tools to design and modify 3d models. Some of the popular options are Autodesk Fusion 360, TinkerCAD, and Blender. There is also other software specific to different types of printers such as the 3d systems software which was acquired by 3d systems. These various tools allow for the creation of a variety of different models and designs. With the right 3d printing software, users can create intricate models, mechanical designs, and functional parts for 3d printing. This allows for the creation of highly customizable designs for 3d printed objects.
10. What is the Future of the 3D Printing Industry?
The future of the 3d printing industry looks bright with ongoing innovations and new applications for the technology. The development of new materials and new 3d printing technologies will continue to expand the applications of this technology. The use of 3d printing to create functional parts and tools will also continue to grow. Furthermore, many believe that 3d printing will accelerate the move towards decentralized production. This will allow for printing closer to the end user, which can greatly speed up delivery times.
The printing process will continue to become more refined as the technology develops, offering higher precision and speed. Furthermore, the use of 3d printing in personalized medicine and bioprinting, printing organs and body parts, is expected to expand. 3d printing could greatly change the manufacturing landscape, allowing for the creation of complex, customized objects on demand. The development of this technology means that the use of 3d printing is poised to greatly change the world. Therefore, the future of the 3d printing industry looks bright with many possibilities.
Summary
- 3d print is an additive manufacturing process that creates three-dimensional objects by layering material based on a 3d model.
- A 3d printer works by depositing layers of material on a build platform according to digital instructions provided from the 3d model.
- Common types of 3d printers include fused deposition modeling (fdm), stereolithography (sla), and selective laser sintering (sls), each using a different 3d printing process.
- The benefits of 3d printing include its ability to create complex geometries, rapid prototyping, customization, and reduced material waste compared to traditional methods.
- 3d printing has a wide range of applications in prototyping, manufacturing, medical, consumer goods, and many other industries.
- Industries such as aerospace, automotive, and medical, are using 3d printing to create functional parts, prototypes, and tools.
- Common 3d printing materials include plastics, resins, metals, ceramics, and composites, chosen based on the requirements of the printing process.
- The cost of a 3d printer has decreased, making it more accessible, and this will continue to make 3d printing more affordable in the future.
- 3d printing software is needed to create the digital 3d models and prepare them for the printer, and can be simple or highly advanced based on the requirements of the project.
- The 3d printing industry is poised for significant growth with continuous advancements in technology, new materials, and wider applications in the future.